For Wise Food Choices – Use the Glycemic Index List!
Foods on the low glycemic index list are delicious! Low glycemic index foods are drippers. They cause a slow rise in blood sugar, instead of a rapid one. This means your body starts to digest the food and breaks it into sugar more slowly and evenly than with other foods. Recall that the glycemic index is a scale from 0 to 100. Low glycemic index foods have a score less than 55.
Our low glycemic index chart shows foods with both low and high glycemic index values – it is a complete list of values. You can find a great video on low glycemic foods here; most of these foods have a glycemic index of 23-45! They are great sources of vitamins, minerals and antioxidants as well.
See the chart below for the glycemic index list of low glycemic foods. We have also prepared a complete glycemic index chart with most foods on it.
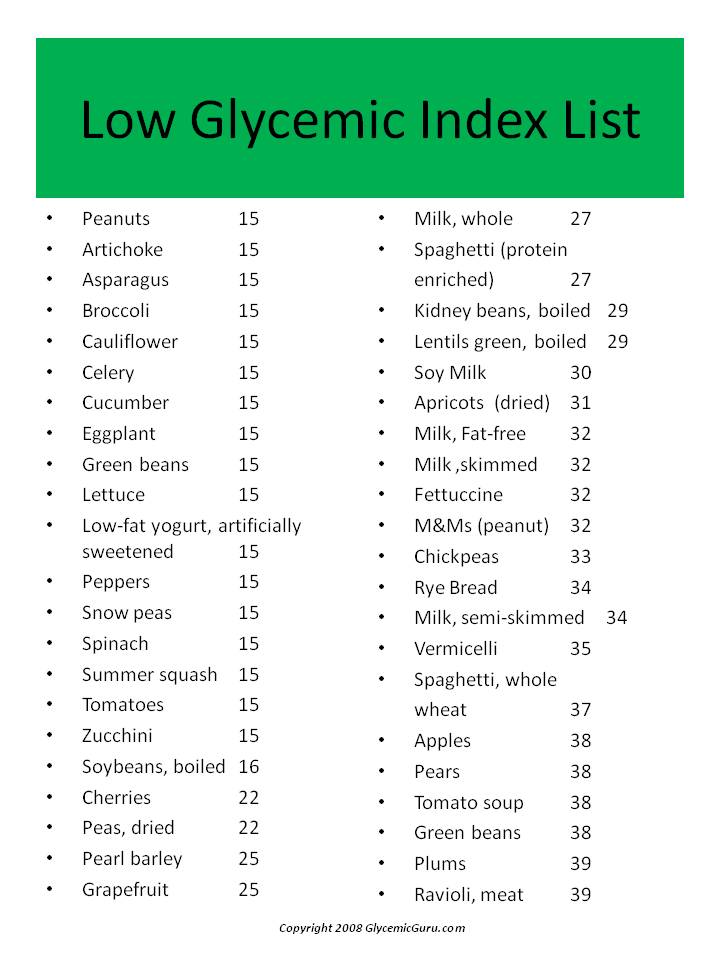
If we consider these foods to be drippers, we could also consider them to be green. Green for go or green for safe. These foods will generally make your blood sugar rise more gradually, which gives your body time to signal for a smaller and more gradual increase in insulin production.
Foods with a glycemic index or GI between 55 and 70 are yellow. Yellow is for caution. These foods will cause your blood sugar to rise more rapidly than the drippers. While these foods are OK in moderation, they are not considered to be low glycemic index foods.
Foods with a GI over 70 are flooders and are red. Red is for warning or stop. These foods tend to cause rapid increases in blood sugar. We call these foods flooders, as they flood your body with sugar and they have a higher potential to cause cell damage due to the high sugar spike. They also cause your body’s insulin level to rise quickly.
Research has shown that consumption of low GI foods leads to:
-improved blood sugar (glucose) control and lipid levels in individuals with diabetes
-better weight control because these foods reduce the appetite and delay hunger
-reduction of insulin levels and fewer spikes of insulin
-a lower incidence of heart disease
-a lower risk of developing Type 2 diabetes
Note that there are many factors that impact the GI. Foods with more fat, higher protein or more fiber tend to have lower GI. Why? The body takes longer to digest these types of foods and thus delays the sugar from entering the blood stream.
An additional note – the values in the table above are averages collected from several sources. Be aware that certain types of foods might have different varieties that will have different GI. We all know that some apples seem “sweeter” than others – a Fuji vs. Granny Smith for example. Further, some GI values can change due to differences in ripeness or age of the food – food can be picked, stored and then consumed a year after picking or the day it was picked – this age impacts the GI, as well as nutritional and vitamin content. A good rule of thumb is to treat the following values as estimates. So if the value in the table is 50, the actual value might vary between 45 and 55.
Call to action: Focus on Low Glycemic Foods
-clean out your pantry, cupboards and grocery food lists of high GI foods
-replace high GI foods with low GI foods
-choose dense, whole grain breads vs. white, light breads
-select high fiber breakfast cereals like oats, barley or bran instead of high sugar cereals
-eat fewer sweets and refined sugar products – soft drinks, desserts, candy bars
In addition to these simple steps, use the low glycemic index list above while shopping or eating out. The shift to low glycemic index foods will give you a fighting chance to improve your health.

